Using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, researchers have discovered that dark energy, a mysterious repulsive force that makes the universe expand at an ever-faster rate, is not new but rather has been present in the universe for most of its 13-billion-year history.Dark energy was already accelerating the expansion of the universe at least as long as 9 billion years ago. This picture of dark energy would be consistent with Albert Einstein's prediction, nearly a century ago, that a repulsive form of gravity emanates from empty space.
Hubble's new evidence is important, because it will help astrophysicists start ruling out competing explanations that predict that the strength of dark energy changes over time.
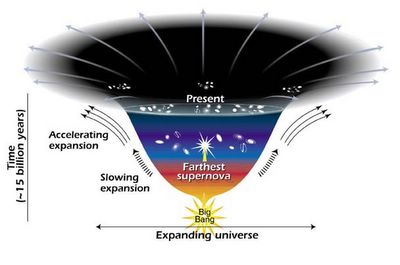
In addition, the researchers found that the exploding stars, or supernovae, used as markers to measure the expansion of space today look remarkably similar to those which exploded 9 billion years ago and are just now seen by Hubble. This is an important finding, say researchers, because it gives added credibility to the use of these supernovae as tools for tracking the cosmic expansion over most of the universe's lifetime. link