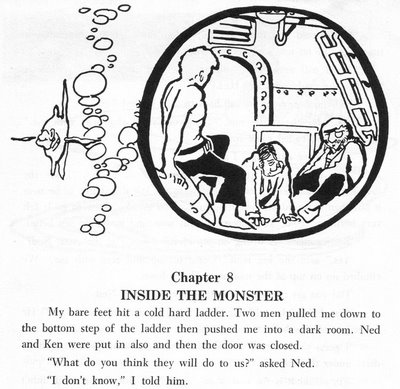
Art © Frazetta
It has been an established fact for several years now that water exists on Mars. However, the big question is how much of it – if any – is in liquid form. The newly discovered deposits were identified by comparing different images of the same area taken by NASA's Mars Global Surveyor (MOC camera), over a period of few years. The images suggest that water may have flowed there sometime within the past seven years.

Photo: NASA/JPL/Malin Space Science Systems
ESA’s Mars Express has found large reservoirs of water underground using its radar experiment MARSIS. All are frozen, with the largest in Mars's polar regions. Such frozen underground lakes might be driven to temporarily thaw and flow across the surface by changes in temperature, caused by changes in illumination from the Sun or, possibly, by local variations in the underground pressure.

Art © Frank Cho
Visit Scenic Barsoom: